上海交大/华中师大张礼知团队PNAS:反向I1Cu4单原子位点高效中性电还原硝酸盐制氨

第一作者:周兵、童雅文
通讯作者:顾向奎、么艳彩、张礼知
论文DOI: 10.1073/pnas.240523612

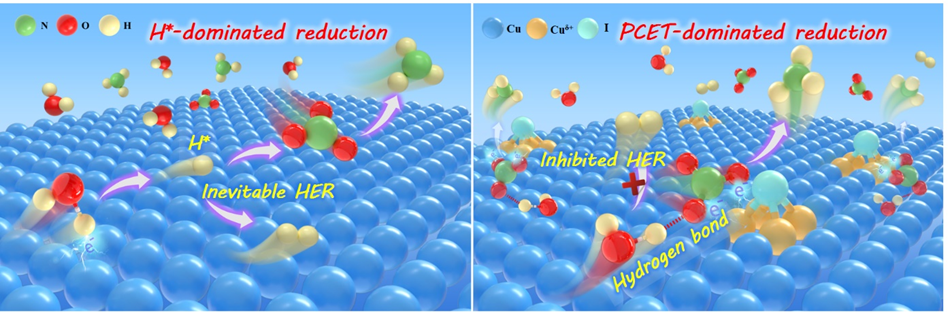


电化学还原硝酸盐合成氨(NITRR)为硝酸盐废水的绿色处理和资源化利用开辟了新的途径。目前,大多数NITRR催化剂通过活性氢(H*)介导的反应机理将NO3−还原为NH3。然而,H*在中性条件下极易偶联生成H2,导致NH3产率和法拉第效率低下。本研究通过在泡沫铜表面锚定碘单原子,构建了一种独特的I1Cu4反向单原子位点。该位点可以通过质子耦合电子转移(PCET)机理驱动NITRR,并在中性条件下实现了4.36 mg h−1 cm−2的氨产率和98.5%的法拉第效率,远超传统Cu位点和大多数H*介导的NITRR催化剂。理论计算表明,I单原子调控配位Cu原子的局域电子结构,通过双电子转移通道促进NO3−的双齿吸附和活化,并抑制H2O吸附解离产生H*,从而将H*介导的反应机理转变为动力学更有利的PCET。利用硝酸盐还原和原位氨回收的流动耦合装置,在1 A cm−2的工业电流密度下,I1Cu4电极获得了69.4 mg h−1 cm−2的氨产率。本研究首次报道了反向单原子位点能通过调控反应机理,极大提升电还原硝酸盐合成氨性能,并为设计高性能电催化剂提供了新策略。

区别于传统的SAC催化剂,其以多个非金属原子(N、C、O)与单个金属位点配位,反向SAC催化剂的非金属原子中心被多个金属位点配位。这将提供丰富的双齿吸附活性位点,通过双电子转移通道去活化NO3−,并借助PCET机制的优势大幅提升NITRR性能。铜(Cu)凭借其独特的3d10电子构型能够比其他金属产生更强的“接受-反馈”相互作用,成为理想的NITRR反应位点。碘(I)因其中等电负性和最弱的氢键因而展现出最强的诱导效应。因此我们将碘单原子锚定在铜表面以构筑反向单原子位点,评估其硝酸根还原性能,并研究反应机理。

电镜表征
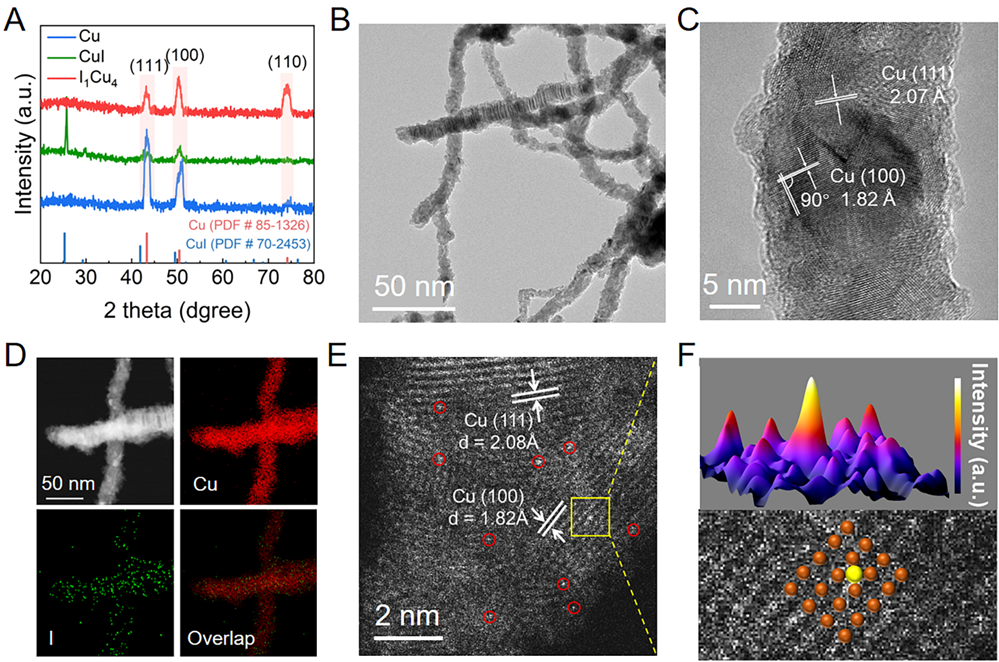
Fig. 1. Synthesis and characterization. (A) GI-XRD patterns of Cu, CuI and I1Cu4. (B) TEM image and (C) HRTEM image of I1Cu4. (D) EDX elemental mapping of I1Cu4. (E)Atomic-resolution HAADF-STEM image of I1Cu4.(F) 3D surface intensity profile (top) and magnified HAADF-STEM image taken from the yellow dashed rectangle in (E) (bottom). Orange and yellow balls represent Cu and I atoms. Copyright 2024, PNAS.
通过在泡沫铜表面原位生长CuI前驱体,然后电化学还原制备反向I1Cu4单原子位点电极。球差电镜结果表明I以单原子形态在金属铜表面均匀分布,并且I单原子可能与四个Cu原子配位。
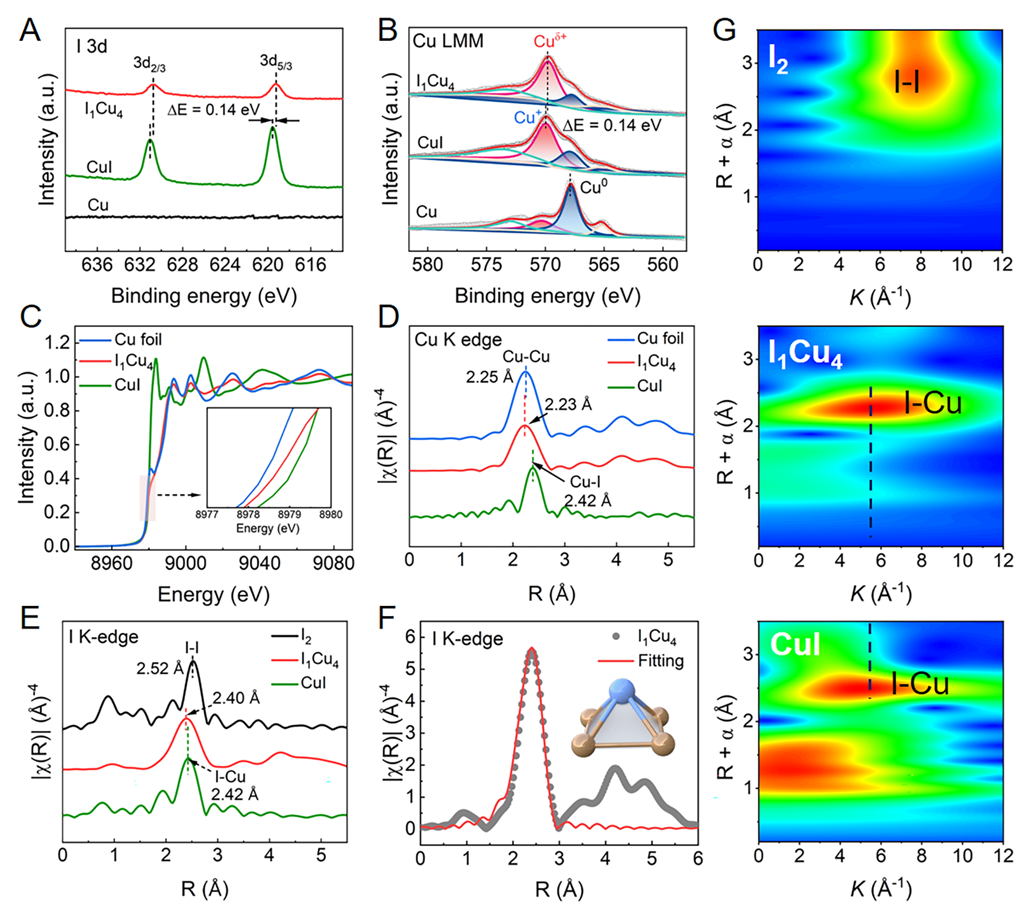
Fig. 2. Chemical state and coordination information of I1Cu4. (A)XPS spectra of I 3d and (B) Cu LMM Auger of Cu, CuI and I1Cu4.(C) Normalized Cu K-edge XANES spectra of Cu foil, CuI and I1Cu4. (D) Corresponding Cu K-edge EXAFS spectra. (E) I K-edge EXAFS spectra of I2, I1Cu4and CuI. (F) Fitting curve of I K-edge EXAFS spectra of I1Cu4at R space, the insert shows the schematic model of I1Cu4.(G) WT-EXAFS contour plots of I K-edge EXAFS data of I2, I1Cu4and CuI. Copyright 2024, PNAS.
NITRR性能测试
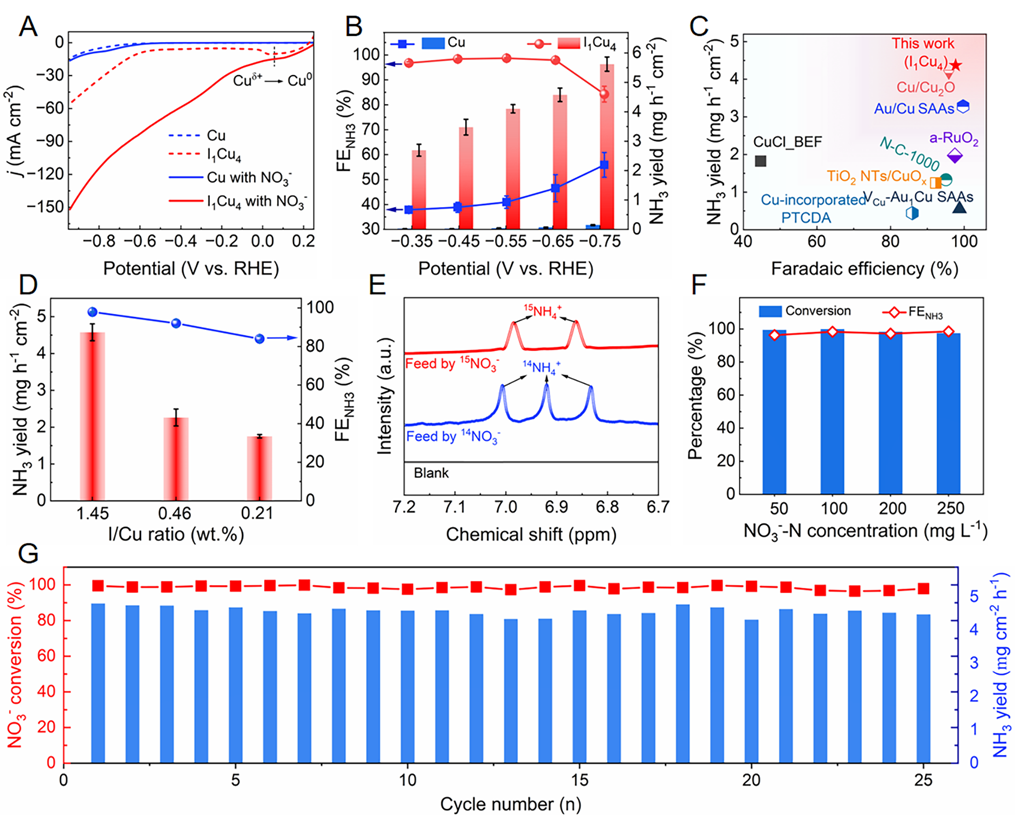
Fig. 3. Electrocatalytic NITRR performance. (A) LSV curves of Cu and I1Cu4in an Ar-saturated electrolyte of 0.5 M K2SO4 with or without 100 mg NO3–-N L–1. (B) FENH3and NH3 yield rate over Cu and I1Cu4 at various working potentials. (C) Comparison of FENH3 and NH3yield rate over I1Cu4 with reported electrocatalysts in neutral media. (D) FENH3 and NH3 yield rate over I1Cu4with different I content. (E) 1H NMR spectra of electrolyte using 14NO3– and 15NO3–as reactants. (F) NO3– conversion efficiency and FENH3 at various initial NO3– concentrations. (G)Cycling tests of I1Cu4 at −0.65 V vs. RHE. Copyright 2024, PNAS.
在中性电解质中,反向I1Cu4单原子位点在-0.65 V vs. RHE下的产NH3速率和法拉第效率分别高达4.36 mg h−1 cm−2和98.5%,优于绝大多数报道的NITRR催化剂。此外,I1Cu4单原子位点的NITRR活性跟I含量成正相关。在25次循环测试中,I1Cu4保持优异的稳定性。
NITRR机理研究
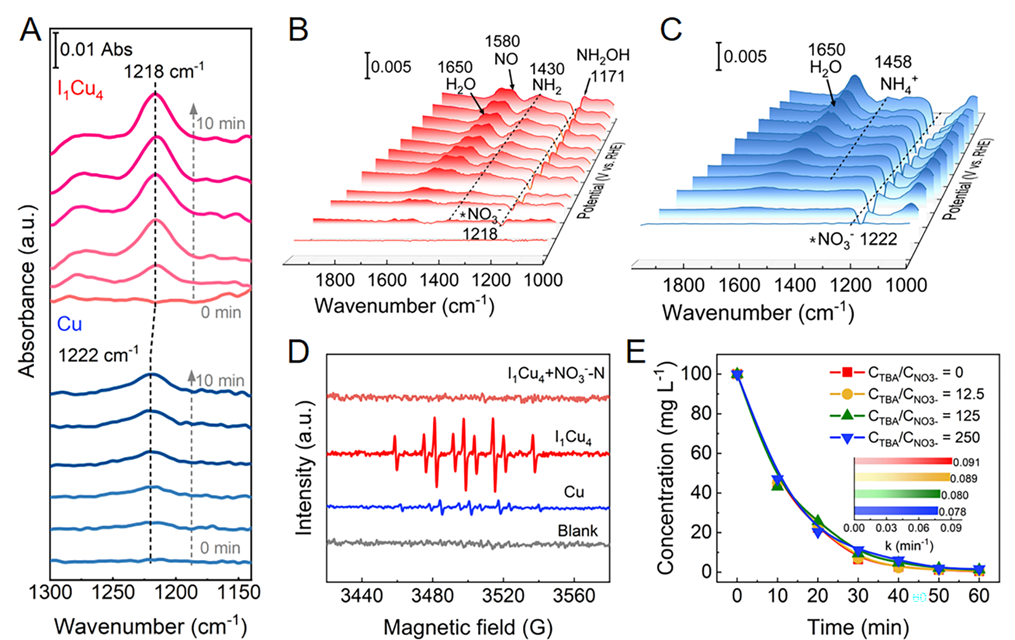
Fig. 4. Mechanistic investigations of NITRR on Cu and I1Cu4.(A) Time-dependent ATR-FTIR spectra of adsorbed NO3−over I1Cu4 and Cu under the open circuit potential. In-situelectrochemical ATR-FTIR spectra collected on (B) I1Cu4and (C) Cu under the potential from OCP to −0.85 V vs. RHE. (D)ESR spectra of DMPO-H* over I1Cu4 and Cu in the presence or absence of NO3−. (E) Effect of different ratios of CTBA/CNO3− on the NO3−conversion activity over I1Cu4 at −0.65 V vs. RHE. Copyright 2024, PNAS.
原位红外光谱(ATR-FTIR)揭示I1Cu4能增强NO3−吸附并抑制H2O吸附。ESR结果表明H*可能参与Cu或I1Cu4电极上的NITRR过程。添加TBA或DMPO显著降低了Cu电极的NO3−转化效率,证实了H*是Cu电极还原NO3−的主要活性物种。然而,TBA和DMPO并不能抑制I1Cu4的NITRR性能,表明PCET是I1Cu4驱动NITRR的反应机制。我们认为I1Cu4的Cuδ+位点优先吸附NO3−,并抑制H2O的吸附解离形成H*,从而将Cu电极上H*介导的还原机制转变为I1Cu4上的PCET还原机制。
NITRR机理转变研究
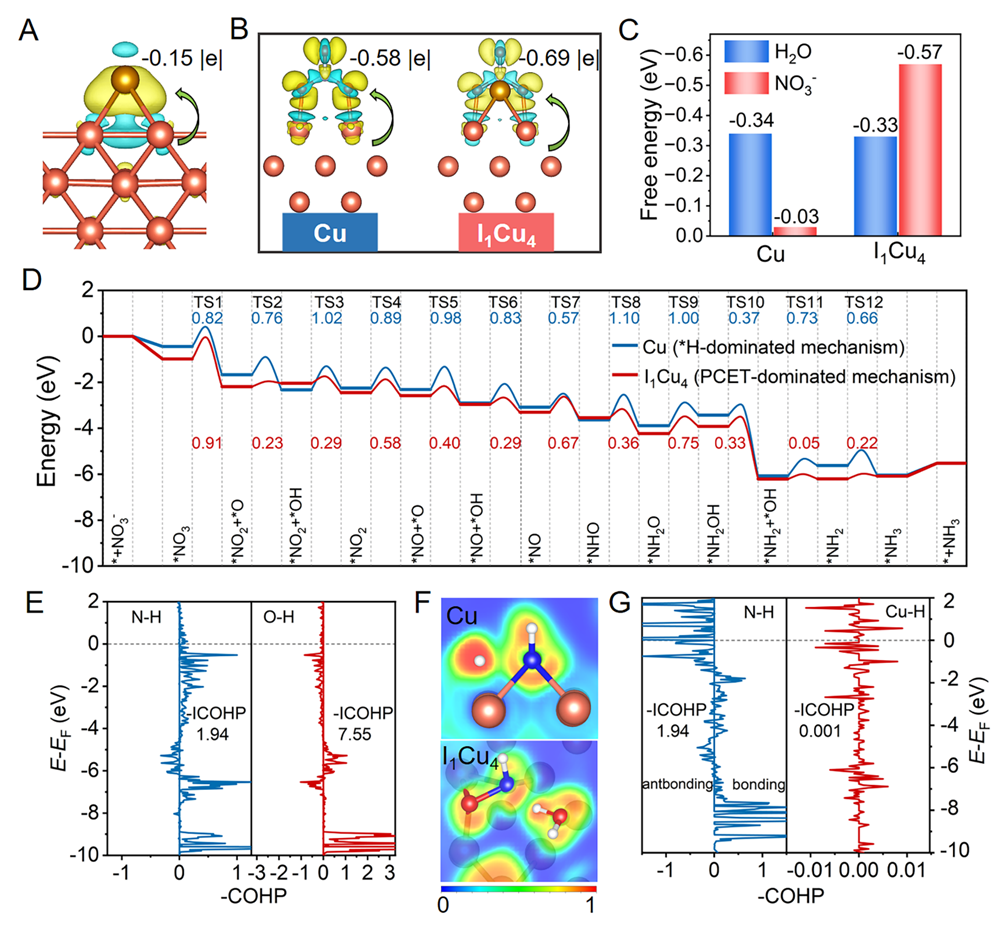
Fig. 5. Theoretical studies of NITRR on Cu and I1Cu4.(A) Charge density difference of I adsorbed on Cu(100). (B)Charge density differences of NO3-adsorbed on Cu and I1Cu4. (C) Gibbs free energy of adsorbed H2O and NO3-on Cu and I1Cu4 at pH = 7. (D) Gibbs free energy diagrams for NITRR on Cu and I1Cu4 via H*-mediated and PCET mechanisms under a potential of 0 V vs. RHE, respectively. (E) ICOHPs for the transition states of the *NHO→*NH2O step on I1Cu4. (F) Electron localization function (ELF) for the transition states of the *NHO→*NH2O step on Cu and I1Cu4. (G) ICOHPs for the transition states of the *NHO→*NH2O step on Cu. The yellow and cyan colors represent the electron accumulation and depletion, respectively. The orange, brown, red, blue, and white spheres represent Cu, I, O, N, and H atoms, respectively. Copyright 2024, PNAS.
理论计算结果证实I1Cu4的Cuδ+位点倾向吸附NO3−而不是H2O,这将抑制H2O解离形成H*,从而有利于PCET机制的发生。反应势能面计算进一步表明I1Cu4以PCET机制驱动NITRR展现出更强的动力学优势。
基于I1Cu4电极的流动耦合装置电化学还原硝酸根和原位回收氨性能测试
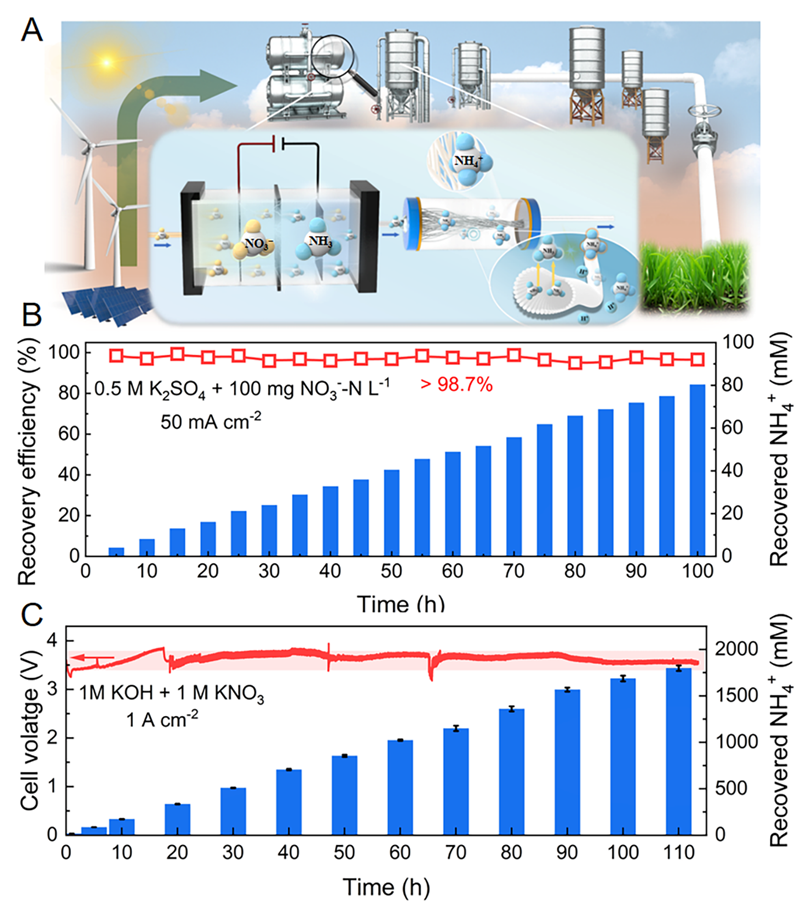
Fig. 6. Application potential of flow-through coupled device based on I1Cu4 electrode. (A) Schematic illustration of flow-through coupled device for continuous nitrate conversion and in-situ ammonia recovery. (B) Recovery efficiency of produced NH3 and concentration of accumulated recovered NH4+of the flow-through coupled device during the stability test in low NO3−concentration (100 mg NO3−-N L−1 +0.5 M K2SO4) at 50 mA cm–2. (C) Cell voltage and concentration of accumulated recovered NH4+ of the flow-through coupled device during the stability test in high NO3−concentration (1 M KNO3 +1 M KOH) at 1 A cm–2. Copyright 2024, PNAS.
将I1Cu4单原子电极集成到用于硝酸盐还原和原位氨回收的耦合装置中,在高浓度硝酸盐溶液中,I1Cu4以1 A cm−2的工业电流密度,稳定运行超110 h,并实现了69.4 mg h−1 cm−2的氨产率。

本工作首次证明了反向I1Cu4单原子位点具备优异的NITRR活性。在中性条件下,其NH3产率达到4.36 mg h−1 cm−2,法拉第效率高达98.5%,超越大多数报道的NITRR电催化剂。研究表明,I1Cu4通过动力学有利的PCET机制而不是H*介导的机制来催化NITRR。具体而言,I单原子触发四个配位Cu原子反应位点的电子离域,促进NO3-的双齿吸附,进而通过双电子转移通道充分活化NO3-,同时抑制H2O吸附和解离来阻止H*的形成。利用流动耦合装置进行连续硝酸盐转化和原位氨回收,I1Cu4可以在110小时内以1 A cm−2的工业水平电流密度保持69.4 mg h−1 cm−2的氨回收产率。本研究通过构筑一种新颖的反向单原子活性位点来调控NITRR机理,实现了中性条件下高效处理硝酸盐废水和合成氨。



么艳彩:上海交通大学环境科学与工程学院副教授、博士生导师。研究方向为单原子催化、环境/能源电化学。尤其关注电催化过程中水分子在钛基单原子电极表面的活化和定向转化过程及水污染控制应用。以第一/通讯作者身份在Nat. Catal.、PNAS、J. Am. Chem. Soc.(2篇)、Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.(4篇)、Environ. Sci. Technol.、Nat. Commun.(3篇)、Water Res.等期刊发表SCI论文20余篇,研究成果被Chemical Review、Chemical Society Reviews、Technology Times、EurekAlert!等国际科学媒体广泛报道,并多次被新华社、人民日报、人民日报(海外版)、人民网、科学网等多家国内外主流媒体关注。授权中国发明专利3项,并成果转化1项。撰写英文专著1部。曾获中科院“百篇优博论文”和中科院院长优秀奖、第7届全国水处理与循环利用学术会议优秀报告奖。先后获得国家自然科学基金、上海市科委面上项目、科技部重点研发计划项目子课题、博士后站前特别资助、博士后面上资助等7项省部级项目资助。现任Colloid and Surface Science编委、National Science Open、EcoEnergy、《环境科学与技术》青年编委。

Permissions for reuse of all Figures have been obtained from the original publisher. Copyright 2024, PNAS
参考文献:
Zhou, B.#; Tong, Y. W.#; Yao, Y. C.*; Zhang, W. X.; Zhan, G. M.; Zheng, Q.; Hou, W.; Gu, X.-K.*; Zhang, L. Z.* Reversed I1Cu4 single-atom sites for superior neutral ammonia electrosynthesis with nitrate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 2024, 121, e2405236121
https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2405236121
转自:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/RkrunNtoWvg-Q2cFwzMO7g

